Introduction: The Allure of Wild Foraged Ingredients in Gourmet Cooking
In recent years, wild foraged ingredients have seen a surge in popularity, particularly in the world of gourmet cuisine. Wild mushrooms, wild berries, and wild vegetables are not only sought after for their distinctive flavors but also for their nutritional benefits and the sense of connection to nature they provide. These ingredients, often seen as the hallmark of Michelin-starred restaurants and exclusive dining experiences, offer a raw and natural element that cultivated produce simply cannot match.
But what makes wild foraged foods so special? Why have these ancient ingredients made such a strong comeback in the world of fine dining? The answer lies in their intense flavors, complex textures, and rich histories—qualities that elevate a dish from ordinary to extraordinary. Whether it’s the earthy, smoky flavor of wild mushrooms, the sweet-tart tang of foraged berries, or the crisp freshness of wild greens, these ingredients allow chefs to create culinary masterpieces that evoke a deeper connection to the land.
In this article, we explore the fascinating world of wild foraged foods—specifically wild mushrooms, wild berries, and wild vegetables. We will delve into their nutritional properties, health benefits, culinary uses, and importance in modern gastronomy. Through understanding the value of these natural ingredients, we’ll see why they have become a beloved part of high-end menus around the world.
1. The Beauty of Wild Mushrooms: A Chef’s Secret Weapon
1.1 The Rich Flavor Profile of Wild Mushrooms
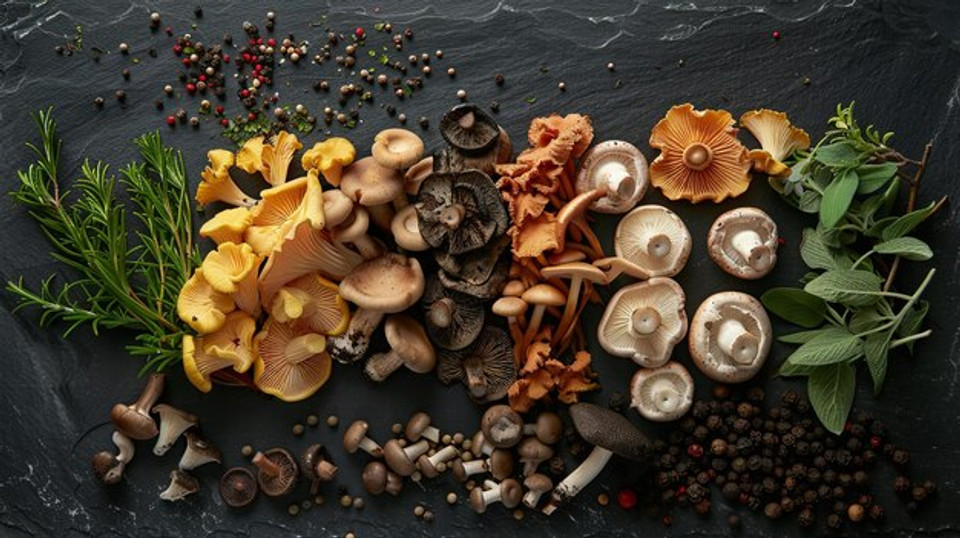
Wild mushrooms have long been prized for their deep, earthy flavors and complex textures. Unlike their cultivated counterparts, wild mushrooms are often more intense in flavor, with variations that range from mild and delicate to bold and robust. The diversity of wild mushroom species offers an endless range of possibilities for chefs, who can incorporate these mushrooms into everything from sauces and soups to grilled dishes and risottos.
Some of the most popular wild mushrooms include:
- Porcini mushrooms: Known for their rich, meaty texture and umami flavor, porcini are often used in Italian cuisine for pasta dishes and sauces.
- Chanterelles: With their delicate, fruity flavor and tender texture, chanterelles are favored in French cuisine for sautés, soups, and sauces.
- Morel mushrooms: These mushrooms are prized for their honeycomb-like appearance and rich, earthy taste. They pair wonderfully with cream-based dishes and wild game.
- Lion’s mane: Known for its shaggy appearance, lion’s mane offers a seafood-like flavor and is often used as a plant-based alternative in dishes like vegan “scallops”.
1.2 The Health Benefits of Wild Mushrooms
In addition to their exceptional flavors, wild mushrooms are also packed with nutrients that can benefit health. Many wild mushrooms are high in vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and dietary fiber. For example:
- Porcini mushrooms are rich in B vitamins, which are essential for energy production and nervous system health.
- Shiitake mushrooms contain lentinans, a type of polysaccharide known for its immune-boosting properties.
- Morel mushrooms are high in iron, which is essential for oxygen transport in the body.
Wild mushrooms also contain compounds like ergothioneine, a powerful antioxidant that has been shown to help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
1.3 Foraging for Wild Mushrooms: A Sustainable Approach
The practice of foraging for wild mushrooms is not only a way to bring fresh, unique flavors into the kitchen, but it also represents a sustainable and eco-friendly approach to sourcing food. Unlike industrial farming, foraging allows us to harvest food without disturbing the ecosystem, as wild mushrooms often grow naturally and are harvested in moderation.
However, foraging for wild mushrooms should be done with care. Some wild mushrooms are toxic or poisonous, and proper identification is crucial to ensure safety. Many professional foragers and chefs undergo specialized training or work with experts to learn how to properly identify wild mushrooms in their natural habitats.
2. Wild Berries: Nature’s Sweet and Tangy Gems
2.1 The Sweet and Tart Appeal of Wild Berries
Wild berries—such as blackberries, raspberries, blueberries, and elderberries—are some of the most versatile and popular wild ingredients in gourmet cooking. Their sweet-tart flavors make them perfect for a variety of dishes, including desserts, salads, jams, sauces, and even savory dishes. Wild berries are also celebrated for their rich colors, which add a visually striking element to dishes.
For instance, wild blueberries are smaller and more intensely flavored than cultivated blueberries. Their rich, tart flavor and antioxidant content make them an ideal addition to smoothies, pastries, and sauces. Wild strawberries, known for their small size and intense sweetness, are often used in garnishes or dessert dishes where their flavor can shine.
2.2 Health Benefits of Wild Berries
Wild berries are considered superfoods due to their impressive nutrient profile. They are rich in vitamin C, fiber, antioxidants, and phytonutrients, which have been shown to provide a variety of health benefits:
- Antioxidants: Wild berries are packed with anthocyanins, powerful antioxidants that help reduce inflammation and protect cells from oxidative stress.
- Immune Boosting: The high levels of vitamin C in wild berries help strengthen the immune system and support collagen production for healthy skin.
- Brain Health: Studies have shown that the polyphenols in wild berries can improve cognitive function and memory, making them a brain-boosting food.
Additionally, wild berries are a natural source of flavonoids and phenolic compounds, which have been linked to heart health, blood pressure regulation, and cholesterol reduction.
2.3 Foraging Wild Berries: Sustainable and Delicious
Just like wild mushrooms, wild berries are often foraged directly from the natural landscape, making them a sustainable food choice. Foraging for wild berries can also foster a deeper connection with the land, as it requires knowledge of the local flora and understanding of the seasonality of various berries.
Wild berries are commonly found in forests, fields, and hedgerows during the late summer and early fall. Foraging them at their peak ripeness ensures that their flavors are maximized and their nutritional benefits are at their highest.

3. Wild Vegetables: Fresh, Crisp, and Full of Flavor
3.1 Exploring Wild Greens and Vegetables
Wild vegetables—such as dandelion greens, nettles, wild spinach, and wild garlic—are prized for their unique flavors and incredible versatility. These vegetables are typically more bitter and robust than their cultivated counterparts, and their distinct taste adds layers of complexity to any dish.
For example, wild garlic (also known as ramps) is often used in high-end restaurants to enhance the flavor of soups, sauces, and pasta dishes. The leaves of wild garlic are garlicky yet milder than cultivated garlic, providing a delicate flavor that pairs well with both vegetarian and meat-based dishes.
Other wild greens like dandelion leaves offer a bitter taste that works well in salads or as a side dish. These greens are often sautéed with garlic and olive oil to balance out their bitterness.
3.2 Health Benefits of Wild Vegetables
Wild vegetables are typically nutrient-dense and low in calories, making them an excellent choice for those seeking to optimize their health. Wild greens, in particular, are rich in vitamins A, C, and K, minerals like iron, and fiber.
- Dandelion greens are known for their detoxifying properties and are rich in antioxidants that support liver health.
- Nettles are packed with vitamins A and C, and their anti-inflammatory properties have been used to treat joint pain and allergies.
- Wild spinach contains high levels of folate and magnesium, which support muscle function and bone health.
These wild vegetables are also high in chlorophyll, a powerful plant compound that can aid in detoxification and digestion.
4. The Importance of Foraged Ingredients in High-End Restaurants
4.1 Why Chefs Choose Wild Foraged Foods
In the world of fine dining, chefs are always searching for ways to elevate their dishes and create something unique. Wild foraged ingredients offer a distinctive edge, providing both flavor and story that cultivated ingredients cannot match. The use of wild ingredients also allows chefs to connect diners to the environment, offering an immersive dining experience that highlights the seasons and the land.
For example, Michelin-starred restaurants often incorporate wild ingredients into their tasting menus, using wild mushrooms or wild herbs to create complex flavor profiles. Chefs also value wild ingredients for their sustainability, as foraging allows them to harvest locally and reduce the environmental impact of industrial farming.
4.2 Foraged Ingredients as a Culinary Trend
In recent years, there has been a growing trend of foraging in the culinary world, with chefs experimenting with wild ingredients to create innovative dishes. Restaurants that specialize in foraged foods may even offer foraging experiences for their diners, where guests can participate in the collection of wild ingredients before sitting down to a multi-course meal that showcases these natural treasures.
5. Conclusion: A Return to Nature’s Bounty
The growing popularity of wild mushrooms, wild berries, and wild vegetables in high-end cuisine signals a shift back to nature. These foraged ingredients are not only flavorful and nutritious but also offer a unique, sustainable, and deeply connected culinary experience. As more chefs and home cooks alike embrace the value of wild foraged foods, these ingredients will continue to play an important role in shaping the future of modern gastronomy.
Whether you are a seasoned chef looking to elevate your dishes, or a home cook eager to explore the world of wild foods, foraging for wild mushrooms, berries, and vegetables offers an exciting and rewarding journey into the world of flavor, nutrition, and sustainability.