Introduction: The Rise of Plant-Based Sweets
The culinary world has witnessed a significant shift toward plant-based eating, driven by health awareness, ethical considerations, and environmental concerns. Vegan desserts—sweets prepared without animal-derived ingredients such as dairy, eggs, or honey—have emerged as a creative and delicious subset of this movement.
Far beyond mere substitutions, vegan desserts leverage the natural flavors, textures, and nutritional benefits of plant ingredients, offering diverse options that satisfy both the palate and the conscience. From rich chocolate cakes made with aquafaba to creamy nut-based cheesecakes, plant-based desserts are now a mainstay in both home kitchens and gourmet restaurants.
This article explores the history, techniques, nutrition, and sustainability of vegan desserts, highlighting the scientific principles behind ingredient choices and culinary creativity.
1. History and Cultural Context of Vegan Desserts
1.1 Early Influences
While modern veganism is relatively recent, plant-based sweets have roots in ancient culinary traditions:
- Asian cuisine: Rice-based desserts, sweet bean pastes, and coconut milk puddings.
- Middle Eastern cuisine: Date-based confections, nut pastes, and syrup-soaked pastries.
- European adaptations: Early forms of dairy-free tarts and fruit compotes for fasting periods.
These early examples demonstrate that vegan sweets are not merely substitutes but often original creations, emphasizing natural flavors and texture contrasts.
1.2 Contemporary Evolution
- 20th century: Vegan desserts were largely niche and often limited in taste and variety.
- 21st century: Innovations in plant-based ingredients such as aquafaba, nut milks, and coconut creams have enabled the creation of desserts that rival traditional ones in texture, richness, and flavor.
- Global influence: The fusion of cultural desserts with vegan techniques has expanded options, from vegan tiramisu to raw chocolate truffles.
2. Core Ingredients in Vegan Desserts
Vegan desserts rely on plant-based ingredients that replicate the functions of eggs, dairy, and butter in traditional baking.
2.1 Egg Substitutes
- Aquafaba: The liquid from cooked chickpeas; excellent for meringues, mousses, and light cakes.
- Flaxseed or chia “eggs”: Ground seeds mixed with water; bind and provide structure.
- Applesauce or mashed banana: Moisture and subtle sweetness; ideal for cakes and muffins.
2.2 Dairy Alternatives
- Plant-based milks: Almond, oat, soy, coconut, and rice milks; each with unique flavor profiles and fat content.
- Nut and coconut creams: Used for frostings, mousses, and custards.
- Vegan butter substitutes: Coconut oil, margarine, and nut butters.
2.3 Sweeteners
- Natural sweeteners: Maple syrup, agave, date syrup, coconut sugar.
- Refined sugars: Used cautiously; some desserts combine multiple sweeteners for balanced flavor and texture.
2.4 Flours and Bases
- Gluten-free flours: Almond, oat, rice, or buckwheat.
- Whole-grain flours: Provide fiber and a nutty flavor.
- Binding agents: Psyllium husk, arrowroot, or tapioca starch.
3. Techniques for Perfect Vegan Desserts
3.1 Achieving Structure and Volume
- Whipping aquafaba with sugar produces stable, airy meringues.
- Baking with chia or flax “eggs” provides elasticity and binding, ensuring cakes rise properly.
3.2 Creating Creaminess and Richness
- Blended cashews or almonds can produce silky, dairy-like textures for cheesecakes and custards.
- Coconut cream adds luxurious mouthfeel and can substitute heavy cream in ganaches and frostings.
3.3 Flavor Enhancement
- Vanilla, cocoa, citrus zest, and spices complement natural sweetness.
- Roasting nuts or fruits enhances aroma and deepens flavor complexity.
3.4 Balancing Moisture
- Plant-based flours and ingredients absorb differently than wheat or dairy; adjusting liquids and fats is crucial.
- Over-hydration or under-hydration can lead to dense or dry desserts; precise measurement is essential.
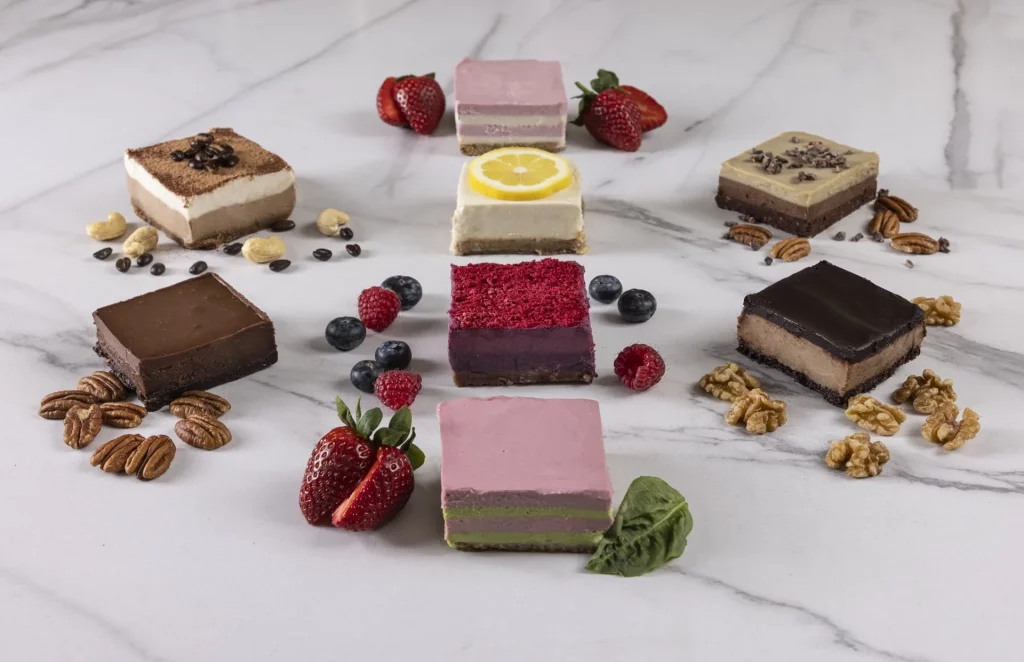

4. Popular Categories of Vegan Desserts
4.1 Cakes and Cupcakes
- Chocolate avocado cake: Creamy texture from avocado; cocoa provides richness.
- Carrot and date cake: Natural sweetness and moisture; often topped with cashew frosting.
- Mini cupcakes: Allow experimentation with flavors like matcha, pumpkin, or citrus.
4.2 Cookies and Bars
- Oatmeal and nut cookies: Use flax “egg” for binding; combine nuts, seeds, and dried fruits.
- Brownies: Replace eggs with silken tofu or black beans for fudgy texture.
- Energy bars: Dates, nuts, and seeds pressed together; no baking required.
4.3 Puddings, Mousses, and Custards
- Chia pudding: Chia seeds absorb plant-based milk, creating a gel-like consistency.
- Aquafaba mousse: Whipped chickpea liquid, chocolate, and sweetener for airy texture.
- Cashew cream custard: Smooth and creamy, ideal for layered desserts.
4.4 Frozen Desserts
- Vegan ice creams: Coconut milk, cashew milk, or oat milk bases; churned or frozen raw.
- Sorbet: Fruit purée and natural sweeteners; refreshingly light.
- Frozen popsicles: Creative combinations of fruit, nut butter, and spices.
4.5 Raw Desserts
- Raw chocolate truffles: Cocoa, nuts, and dates; no baking needed.
- Raw cheesecakes: Cashew or almond bases, often sweetened with agave or dates.
- Layered raw tarts: Crust of nuts and dried fruit, topped with blended fruit or chocolate.
5. Nutritional Aspects of Vegan Desserts
5.1 Health Benefits
- Lower saturated fat: Coconut, nut, and seed fats are healthier alternatives to butter.
- High fiber: Whole grains, nuts, and fruits increase fiber content.
- Micronutrients: Nuts, seeds, and fruits provide vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.
5.2 Considerations
- Vegan desserts can still be calorie-dense; portion control is important.
- Balancing sugar, fat, and protein ensures satisfying yet nutritious options.
5.3 Functional Ingredients
- Cacao: Antioxidants and mood-boosting compounds.
- Turmeric or ginger: Anti-inflammatory effects in spiced desserts.
- Nuts and seeds: Healthy fats, magnesium, and protein.
6. Sustainability and Ethical Implications
6.1 Environmental Benefits
- Plant-based desserts require fewer resources than dairy-based equivalents:
- Lower water consumption
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions
- Less land usage
6.2 Ethical Considerations
- No animal exploitation; aligns with vegan and ethical food movements.
- Encourages conscious consumption and mindful sourcing.
6.3 Zero-Waste Opportunities
- Use fruit peels for zest
- Overripe bananas or apples in baking
- Nut pulp from plant-based milk production in cookies or bars
7. Culinary Creativity and Presentation
7.1 Flavor Pairings
- Chocolate and raspberry, lemon and coconut, or matcha and white chocolate flavor combinations.
- Layering textures: crunchy nuts, creamy fillings, and soft cake layers.
7.2 Visual Appeal
- Use natural colors from fruits, spirulina, beetroot, and turmeric.
- Garnishes: toasted seeds, edible flowers, cacao nibs, and fruit slices.
7.3 Advanced Techniques
- Vegan tempering for chocolate work
- Plant-based piping creams
- Molecular gastronomy-inspired vegan desserts
8. Future Trends in Vegan Desserts
- Functional desserts: Incorporating adaptogens, protein, and probiotics.
- Artisan chocolate and nut-based treats: Focus on ethical sourcing and single-origin ingredients.
- Hybrid desserts: Combining traditional dessert aesthetics with plant-based innovations.
- Global fusion: Veganizing desserts from different cultures, e.g., tiramisu, gulab jamun, or flan.
9. Practical Tips for Home Baking
- Always weigh plant-based ingredients for consistency.
- Experiment with binding agents; adjust based on texture desired.
- Roast nuts and seeds for enhanced flavor.
- Store properly: many vegan desserts (especially raw) require refrigeration or freezing.
- Taste frequently and balance flavors with acid (citrus), sweetness, and salt.
10. Conclusion: Redefining Sweet Indulgence
Vegan desserts embody creativity, nutrition, and sustainability. They challenge traditional notions of sweetness, proving that indulgence does not require animal products. By leveraging plant-based ingredients, bakers and chefs can craft desserts that are:
- Deliciously innovative
- Nutrient-rich
- Environmentally responsible
- Ethically aligned
As plant-based culinary innovation continues to grow, vegan desserts are poised to become mainstream favorites, demonstrating that conscious choices can be both pleasurable and sustainable.
Embracing vegan desserts allows for a holistic approach to indulgence, uniting taste, health, and environmental mindfulness. Every cake, cookie, mousse, or truffle becomes an opportunity to celebrate plant-based creativity.